Age-appropriate testing can ensure the best possible outcomes and quality of life for even the youngest cochlear implant candidates who may have abnormal balance and equilibrium function.
By Richard E. Gans, PhD
Investigations regarding the viability of cochlear implants (CI) began in the 1960s and 1970s. But it was in the early 1980s that CIs became widely embraced, and have since grown in application, acceptance, and utilization, with FDA approval in 1984 for adults and 1990 for children. According to the NIDCD(1), most recent statistics, as of 2019, there have been 736,900 individuals implanted worldwide. In the United States there have been 118,100 and 65,000 implantations for adults and children, respectively. Recently the age for pediatric CI has been reduced from 1 year to 9 months of age.(2)
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, an estimated three in 1,000 infants are born in the United States each year with moderate, severe, or profound hearing loss.(3) Hearing loss is the most common congenital condition in the U.S.(4) There are over 500 syndromes, non-syndromes, and mitochondrial heritable conditions with audio-vestibular expressivity, with many having greater vestibular expressivity.(5) The most common conditions causing bilateral audio-vestibular loss or hypofunction are listed in Table 1.
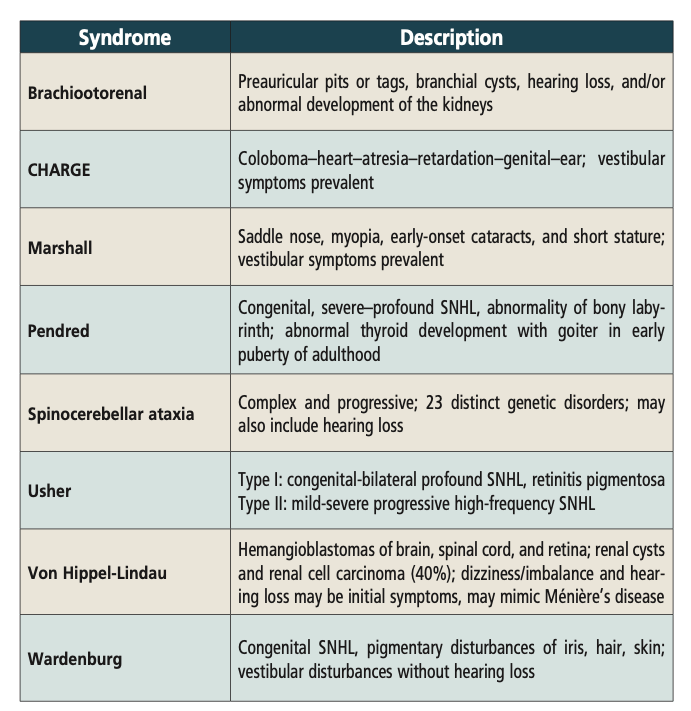
Table 1. Congenital genetic conditions with auditory-vestibular expressivity
Vestibular Function Assessment of Infants
The concern over vestibular and balance function is not due to the CI itself, but those congenital conditions that have vestibular as well as auditory expressivity.
Numerous investigators have published data indicating that the CI is not a causation of vestibular loss. In fact, it has been the anecdotal observation that some CI patients’ balance improved post-CI that has led to the investigations and encouraging preliminary reports of the success of the combined cochlear-vestibular implants in adults.
Further reading: A Better Way to Care for Cochlear Implant Patients
With implantations now being performed at younger ages, as early as 9 months, the infant may not yet be at an age where their delayed motor milestones and any equilibrium dysfunction has yet evidenced itself to parents or caregivers, as they face the challenges of an infant with hearing loss and the hopes of a forthcoming cochlear implant. Just as for decades prior to neonate hearing screening the parents of even profoundly deaf children were told by well-intentioned practitioners “not to worry, he/she will talk when they’re ready,” the same is true for infants and young children who may be quite delayed in their motor development due to lack of vestibular function. Table 2 provides an overview of normative maturational motor development. This will provide practitioners, family, and caregivers a guideline by which to monitor the infant’s development.
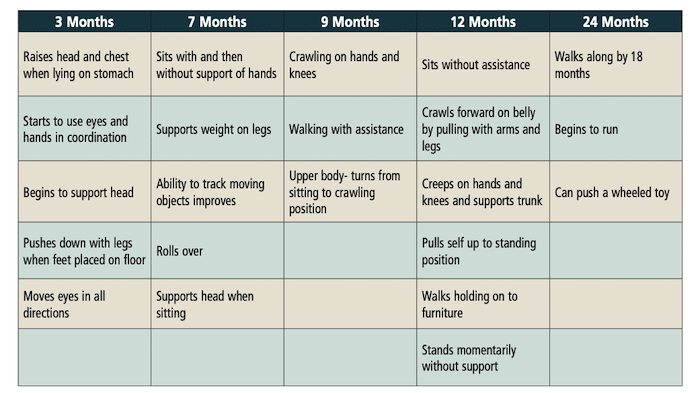
Table 2. Overview of maturational milestones 3-24 months of age
How to Test Infants
In addition to observation and recording of the infant’s motor milestones, infants can be tested with standardized electrophysiological tests as young as 3 months of age with cervical VEMP (cVEMP) testing. There have been numerous publications with normative data for infants through adolescents. This author has found through testing hundreds of infants over 20 years, that it is easy, quick, and comfortable for the infant. As the cVEMP (cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potential) requires the infant to be awake and active, it is much easier than the protocols and requirements for brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER) testing or hearing threshold determination. Video head impulse testing (vHIT) has also demonstrated excellent sensitivity for vestibular function in infants and young children and can be easily administered using a fun, game-like approach for infants as young as 9-10 months of age.
The key to successful vestibular assessment of infants and young children is to be sure that age-appropriate assessment is being undertaken. We have often heard clinicians state that they could not test a child because they were too young for a VNG. Exactly! We should not delay evaluations because a clinic or practitioner does not have either the necessary competency or instrumentation to conduct age-appropriate evaluations. Table 3 provides a summary of age-appropriate protocols for ages 3 months to 60 months old.
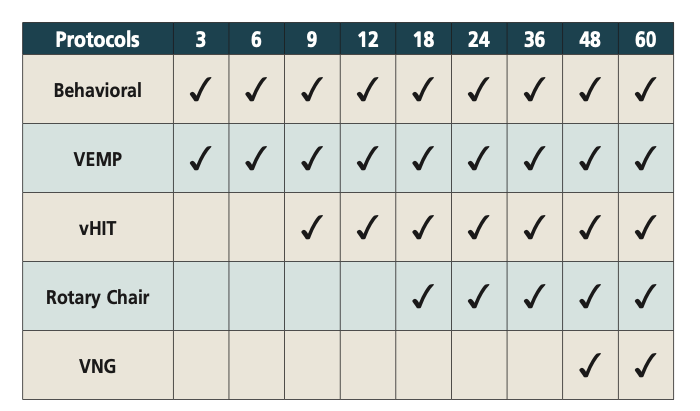
Table 3. Age-appropriate protocols for 3-60 months of age
Habilitation of Infants and Young Children
Now the question is, what if the infant or young child does have a bilateral vestibular loss in addition to the bilateral sensorineural hearing loss requiring the CI? What do we do? Unlike an acquired unilateral vestibular loss or hypofunction, bilateral systemic vestibular loss, the individual cannot have completely normal equilibrium function. They will always be strongly visually and surface dependent, so their lifestyle and activities will need to accommodate these functional limitations. While the combined CI vestibular implant is on the horizon, it is still in the very early stages of development.
Further reading: Neuroplasticity Can Improve Cochlear Implant Effect on Hearing
Pediatric physical and occupational therapy and family involvement and participation is the historical clinical pathway for these children. It is also important to address any other conditions that may co-exist and affect the progression of therapy and maturational norms. This is often seen with premature infants, especially with low birth weights and other modality challenges, e.g., low vision and low muscle tone, who will be playing catch-up in addition to the auditory vestibular deficits. The rigors of scheduling and cost of physical therapy in addition to the speech and language habilitation therapy for the CI may place challenges and hardship on the child’s family.
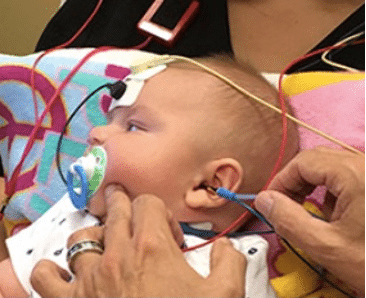
cVEMP is shown being performed on a 3-month-old. Infants can be tested as young as 3 months of age with cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potential. The author has found that it is easy, quick, and comfortable for the infant.
Summary
There are over 500 heritable conditions with auditory vestibular expressivity. It is estimated that as high as 20% to 80% of infants identified with bilateral sensorineural hearing loss and candidates for CI may also have a concomitant bilateral vestibular loss or hypofunction.(6) When a child is identified as a candidate for CI, it is incumbent on practitioners to also evaluate the child’s vestibular function. Abnormal balance and equilibrium function can be addressed and treated in parallel with the CI and subsequent therapy, and should not be delayed. Quality of life and the child’s safety and well-being are as important as normal speech and language development.
Featured image: Video head impulse testing (vHIT) has demonstrated excellent sensitivity for vestibular function in infants and young children and can be easily administered using a fun, game-like approach for infants. This shows how vHIT was adapted for children 24-36 months of age. Photo: Richard Gans
About the author: Richard E. Gans, PhD, is the founder and CEO of the American Institute of Balance (AIB). He is a research scientist member of the American Academy of Neurology, a scientific fellow member of the American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, and a past president of the American Academy of Audiology
References:
- NIDCD Cochlear Implants NO. 00-4798 Statistics Updated 2021
- Karltorp E, Eklöf M, Östlund E, Asp F, Tideholm B, Löfkvist U. Cochlear implants before 9 months of age led to more natural spoken language development without increased surgical risks. Acta Paediatr. 2020 Feb;109(2):332-341. doi: 10.1111/apa.14954. Epub 2019 Sep 10. PMID: 31350923.
- Program to Enhance the Health & Development of Infants and Children (PEHDIC) [Internet]. American Academy of Pediatrics; c2020 [cited 10 Feb 2020]. Available at: https://www.aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/aap-health-initiatives/PEHDIC/Pages/Early-Hearing-Detection-and-Intervention.aspx
- Korver AM, Smith RJ, Van Camp G, Schleiss MR, Bitner-Glindzicz MA, Lustig LR, Usami SI, Boudewyns AN. Congenital hearing loss. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017 Jan 12;3:16094. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.94. PMID: 28079113; PMCID: PMC5675031.
- Gans RE, Evaluation and Management of Vestibular Function in Infants and Children with Hearing Loss. In Madell, Flexer, Wolfe and Schaffer (Eds) Pediatric Audiology: Diagnosis, Technology, and Management 3rd Edition, Theime Publications, New York NY, 2018
- Deng J, Zhu Q, Zhang K, Xie D, Wu W. Vestibular function in children with cochlear implant: Impact and evaluation. Front Neurol. 2022 Aug 23;13:938751. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.938751. PMID: 36090862; PMCID: PMC9449973.





