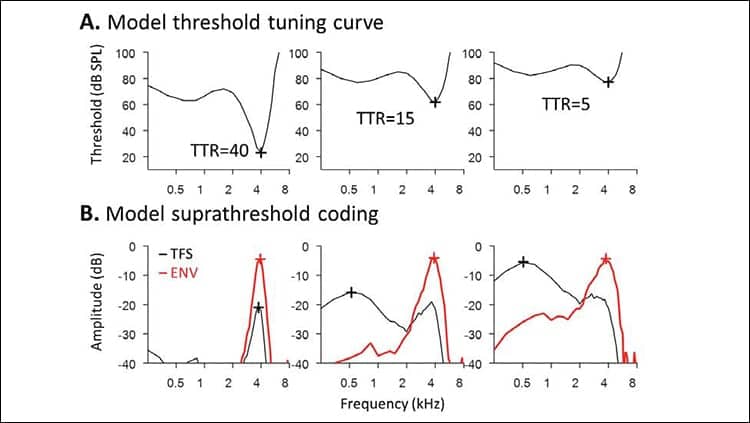
The most common causes of hearing loss—age and excessive noise—have different effects on sound processing in the brain, reports a new study in JNeurosci, the Society for Neuroscience announced. This finding suggests each type of hearing loss should have its own unique treatment.
Michael Heinz, Kenneth Henry, and colleagues used a chinchilla model of age-related hearing loss to observe how the auditory nerve encodes sounds. Comparing their results to data from a noise-induced hearing loss chinchilla model, the researchers found that the same level of sound sensitivity loss caused more severe processing changes in the auditory nerve of chinchillas with noise-induced hearing loss. Additionally, mild noise-induced hearing loss caused the same amount of processing impairment as moderate to severe age-related hearing loss. These findings indicate a need for hearing safety awareness, as well as more refined treatments for each type of hearing loss.
Original Paper: Henry KS, Sayles M, Hickox AE, Heinz MG. Divergent auditory-nerve encoding deficits between two common etiologies of sensorineural hearing loss. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2019;0038-19. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0038-19.2019
Source: Society for Neuroscience, The Journal of Neuroscience
Image: Society for Neuroscience