Split-processing in Hearing Aids Reduces Neural Signatures of Speech-in-Noise Listening Effort
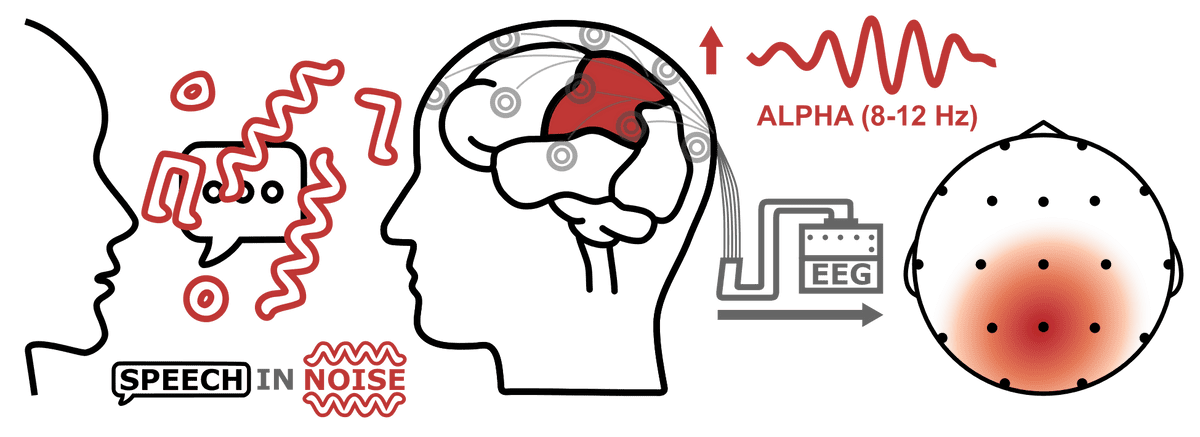
This study uses the electroencephalogram (EEG) and synchronous “alpha” activity over the parietal lobe of the brain to assess listening effort. The researchers find that the intelligibility advantages offered by Signia Augmented Focus hearing aids lead to less effortful listening across a range of SNRs typical of difficult listening environments.